Study Guide
Field 046: Science—Physical Science
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
The following reference material will be available to you during the test:
Objective 0001
The Nature and Processes of Science (Standard 1)
1. As scientists in the twentieth century worked to develop a model of the atom, which of the following best describes a common strategy they employed?
- They disregarded the work of previous researchers in developing their own unique ideas.
- They used mathematical analysis in place of empirical methods to develop their theories.
- They compared the data generated by their experiments against the predicted results.
- They proposed ideas from outside the field of physics to challenge conventional perspectives.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the formulation of testable hypotheses and the principles and procedures for designing and conducting scientific investigations. Like scientists in many other fields, the scientists investigating the nature of matter during the twentieth century evaluated their ideas by comparing the results of their experiments to the experimental outcomes predicted by their various models.
Objective 0002
Central Concepts and Connections in Science (Standard 2)
2. While studying the reactants and products of chemical reactions such as combustion, the eighteenth-century scientist Antoine Lavoisier conducted pioneering studies in stoichiometry. His efforts to quantify the reactants and products of chemical reactions led Lavoisier to prove which of the following?
- Matter is conserved in chemical reactions.
- Energy is produced during combustion reactions.
- Chemical reactions produce new compounds.
- Combustion increases the entropy of a system.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the historical development of important ideas in science from different periods and cultures. Antoine Lavoisier is one of the first chemists to precisely measure the reactants and products in combustion reactions and publish his work. This work provided evidence that although some substances may not be easily accounted for (e.g., a gas given off during a combustion reaction), matter is always conserved in chemical reactions.
Objective 0003
Atomic Structure, the Properties of Matter, and Nuclear Processes (Standard 3)
3. Which of the following best describes how the quantum mechanical model of the atom differs from the Bohr model of the atom?
- It takes into account the wave properties of electrons.
- It focuses primarily on the movement of electrons in the hydrogen atom.
- It proves that electrons can both absorb and emit energy.
- It reveals that different energy levels contain a defined amount of energy.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics and arrangement of subatomic particles and historical and contemporary models of the atom. Although the Bohr model of the atom accounted for the stability of atoms and the quantization of energy in discrete packets, the quantum mechanical model of the atom introduced the idea that particles with mass, such as electrons, can have both wave and particle properties.
Objective 0003
Atomic Structure, the Properties of Matter, and Nuclear Processes (Standard 3)
4. Use the configuration below to answer the question that follows.
1s22s22p63s1
The ground state electron configuration for sodium is shown. Given this information, which of the following can be concluded about the distribution of electrons in the sodium atom?
- Five electrons are unpaired electrons.
- More electrons are located in p orbitals than in s orbitals.
- All of the electrons are located far from the nucleus.
- Twelve electrons are located in p orbitals.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of atomic orbitals and the electron configuration of atoms and ions. In quantum mechanics, electron configurations are used to represent the distribution of electrons. The number of electrons in a particular orbital is designated by the superscripted number to the right of the letter designating the particular orbital. In the example given in the question, there are 5 electrons in s orbitals and 6 electrons in the p orbital.
Objective 0004
Chemical Bonding, Chemical Reactions, and Stoichiometry (Standard 4)
5. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
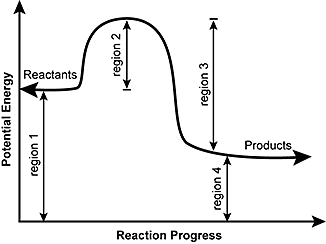
The potential energy diagram for a reaction is shown. Which of the following regions of the curve would be most affected by the addition of a catalyst to the reaction mixture?
- region 1
- region 2
- region 3
- region 4
- Answer
-
Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the principles of chemical kinetics and chemical equilibrium. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Region 2 shown in the diagram depicts the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. By introducing a catalyst to the reaction mixture, the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed is lowered.
Objective 0004
Chemical Bonding, Chemical Reactions, and Stoichiometry (Standard 4)
6. Use the equation below to answer the question that follows.
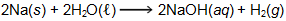
How many grams of H2 will be produced when 5.00 g of Na are reacted according to the chemical equation shown?
- 0.109 g
- 0.220 g
- 1.24 g
- 2.50 g
- Answer
-
Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the mole concept and its use in chemical calculations. To calculate the grams of H2 that will be produced when 5.00 grams of Na are reacted, the following calculations are carried out.
First the number of moles of Na reacted is calculated:
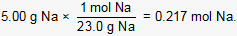
Next, the stoichiometric relationship between Na and H2 is used to calculate the moles of H2 produced when 0.217 moles of Na reacts completely:
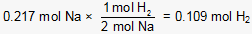
Finally, the number of grams of H2 produced is calculated:
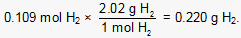
Objective 0005
Energy Transformations, Energy Transfers, and Thermochemistry (Standard 5)
7. Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
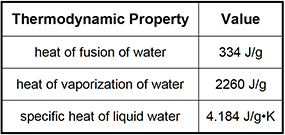
How much heat is absorbed by a 41 g sample of H2O when its temperature is raised from 15°C to 25°C?
- 1.7 kJ
- 2.5 kJ
- 4.3 kJ
- 6.9 kJ
- Answer
-
Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the concepts of heat and temperature and the principles of calorimetry. Raising the temperature of water from 15°C to 25°C does not involve a phase change. As a result, the formula q = mSΔT can be used to calculate the amount of heat absorbed by the 41 g of H2O. In this example, the mass of water (m) is 41 g, the specific heat of liquid water (S) is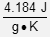
and the change in the sample's temperature (ΔT) is 10°C. The temperature difference in kelvins is equivalent to the temperature difference in degrees Celsius because the two scales have units of equal magnitude. The amount of heat absorbed by the sample is calculated as follows: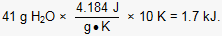
Objective 0005
Energy Transformations, Energy Transfers, and Thermochemistry (Standard 5)
8. Use the equation below to answer the question that follows.
ΔG° = ΔH° – TΔS°
The equation shown can be used to calculate the free energy change for a chemical reaction. Chemical reactions with positive ΔG° values are nonspontaneous, while those with negative ΔG° values are spontaneous. Given this information, which of the following best describes the spontaneity of a reaction with the values ΔH° = 178 kJ/mol and ΔS° = 161 J/K•mol?
- The reaction is nonspontaneous only at high temperatures.
- The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
- The reaction is nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
- The reaction is spontaneous only at high temperatures.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of free energy and the spontaneity of chemical reactions. The spontaneity of the reaction can be assessed by substituting the values of ΔH° and ΔS° into the equation for free energy change and then evaluating the temperature at which the reaction becomes spontaneous. Before doing this, however, the units for both ΔH° and ΔS° need to be the same. When these values are substituted into the equation, it is determined that temperatures greater than 1,105.6 K are required for the value of ΔG° to be less than zero. This determination indicates that the reaction is spontaneous only at high temperatures.
Objective 0006
Motion and Forces (Standard 6)
9. An object is thrown into the air at a 45° angle. If air friction is negligible, the horizontal velocity of the object will:
- equal the vertical component of velocity during the entire trajectory.
- reach a maximum at the peak of the trajectory.
- be constant throughout the entire trajectory.
- reach a minimum at the end of the trajectory.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of Newton's laws of motion and universal gravitation and their application. If the slowing effect of air resistance is disregarded, the horizontal component of the thrown projectile's velocity is the same as the horizontal motion of an object sliding freely on a frictionless surface. Because no force is acting horizontally on the sliding object, it moves at a constant velocity as a result of its inertia. Similarly, the horizontal component of the projectile's velocity also remains constant.
Objective 0006
Motion and Forces (Standard 6)
10. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
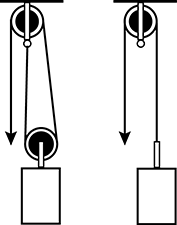
A pulley is being designed to lift heavy objects an upward distance of 40 centimeters. Which of the following values is the same for the two pulley designs shown in the diagram?
- the amount of work needed to lift an object up 40 centimeters
- the minimum force required to make an object move upward
- the length that the rope must be pulled to move an object up 40 centimeters
- the maximum weight of an object that can be lifted with a given applied force
- Answer
-
Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics and uses of simple machines. Work is the product of a force acting on an object and the distance through which the object moves (W = Fd). Although the force needed to lift the object with the two-wheel pulley is less, the force must be applied over a greater distance as the pulley cable is longer. This means the same amount of work will be done lifting the object with either pulley.
Objective 0007
Mechanical Waves (Standard 7)
11. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
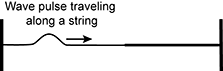
Two strings are the same length, but one of the strings has half the mass of the other. The two pieces of string are attached together to create one length of string. The resulting piece of string is fixed at both ends and tightened. An upright wave pulse is sent down the less massive section of the string, as shown in the diagram. Which of the following describes how the wave pulse will propagate when it reaches and travels along the more massive section of the string?
- The wave pulse will be inverted and have a higher frequency.
- The wave pulse will be inverted and have a greater amplitude.
- The wave pulse will be upright and have a smaller wavelength.
- The wave pulse will be upright and have a slower velocity.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of characteristics of energy transfer by mechanical waves in air, water, and Earth materials. The initial wave pulse will exert a force on the more massive section of string in the upward direction, resulting in an upright wave pulse. The velocity of the wave will be reduced as it encounters and travels through the more massive section of the string because the speed of a wave on a string varies inversely with the string's mass.
Objective 0008
Electromagnetic Energy, Electricity, and Magnetism (Standard 8)
12. Which of the following statements best describes how microwave ovens heat food using electromagnetic waves?
- The electromagnetic waves cause polar molecules to rapidly and repeatedly realign themselves, generating heat through friction.
- Microwaves have enough energy to ionize water molecules, causing them to lose an electron and give off heat energy.
- The electromagnetic waves cause polar molecules to repeatedly change phase from liquid to vapor, generating high-temperature steam.
- Microwaves induce the flow of charge in conductive materials, producing heat from food's resistance to electric current.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the refraction, absorption, and reflection of electromagnetic waves. Microwave ovens generate microwave radiation that heats food by heating the water in the food. This heats all the adjacent food molecules as the increased kinetic energy of the water molecules is transferred to surrounding food particles. The microwaves are able to increase the kinetic energy of the water molecules in food because water molecules are electric dipoles that oscillate when in the oscillating electric field.
Objective 0008
Electromagnetic Energy, Electricity, and Magnetism (Standard 8)
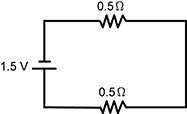
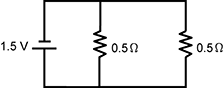
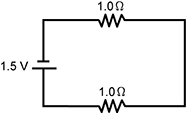
13. Which of the following circuits has the greatest current?
- Answer
-
Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of electricity, electric current, potential difference, resistance, and parallel and series circuits. Ohm's law states that current = voltage/resistance (I = V/R), so the circuit with the least resistance will have the greatest current. In parallel circuits, the total resistance in the circuit is calculated by adding the reciprocals of the resistances of all components and then determining the reciprocal of the sum. In a series circuit, the total resistance is determined by adding the resistances in the circuit. For this reason, a series circuit with two resistors has greater resistance than a parallel circuit with the same two types of resistors.
Objective 0009
Energy and Society (Standard 9)
14. Use the information below to answer the question that follows.
In 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig, operating at a water depth of 5000 feet, exploded and sank into the Gulf of Mexico. Over a three-month period, a variety of approaches were used to try to stop the flow of oil from the wellhead. By the time the flow of oil was successfully stopped, 4.9 million barrels of crude oil had been released into the ocean environment. This event was a devastating environmental and economic disaster for the entire Gulf Coast region.
The description provided of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill illustrates which of the following about the extraction of oil from the environment?
- The development of protocols proven to work in response to accidents in inhospitable environments is just as important as the technological innovations that allow for extraction in these environments.
- Land-based oil exploration should be expanded because the extraction of oil from ocean environments is a new practice with an unproven track record.
- The U.S. government, which leases oil exploration and extraction rights to oil companies, should seek the approval of states potentially affected by an environmental disaster after issuing a lease.
- Operating an offshore oil rig in a manner that minimizes risk is costly and cuts into the already-slim profit margin companies get from selling the extracted crude oil.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the benefits and risks associated with the extraction, use, and management of nonrenewable energy resources, such as coal, oil, natural gas, and uranium. The Deepwater Horizon oil rig used newly developed technologies to drill an oil well 5,000 feet below the surface of the Gulf of Mexico. Although the technology was tested and theoretically safe, a series of events occurred that led to an explosion that killed workers and seriously damaged the well, causing a massive marine oil spill. The information in the passage indicates that although the oil industry had the technology to build the well, it did not have suitable protocols in place to respond quickly and effectively to a disaster of this scale in 5,000 feet of water.
Objective 0010
Science Instruction and Assessment (Standard 10)
15. A physical science teacher decides to introduce the study of the atomic nucleus and radioactivity with a presentation on the use of radiocarbon dating in archaeology. After a short video clip on the topic and a presentation on the process of radioactive decay, students will calculate the age of an ancient skeleton using the half-life of carbon-14 and the amount of carbon-14 that was actually found in the skeleton. This instructional strategy is an effective way to introduce students to the content because it:
- provides a connection to social science curricula that can broaden awareness of the importance of physical science.
- uses a real-world example that can increase the interest and motivation of students.
- reduces the negative connotations surrounding the topic by highlighting a positive use of radioactive isotopes.
- gives students ample time to absorb the content before testing their comprehension with an activity.
- Answer
-
Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of strategies and skills for planning and designing science instruction, including the use of techniques and approaches that meet the needs of diverse learners. The use of real-world examples that hold intrinsic interest for students is an effective way to introduce difficult topics that involve abstractions, such as the nature of the atomic nucleus and radioactivity. This strategy can help motivate students if the real-world example is of interest to them. Even if the example is not intrinsically interesting to them, introducing a real-world example demonstrates the relevance of the topic outside of the classroom. The increased motivation will support student learning as they struggle with difficult or abstract physical science topics.