Study Guide
Field 045: Science—Life Science
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
Objective 0001
The Nature and Processes of Science (Standard 1)
1. A medical researcher hypothesizes that the increased frequency of asthma in adults living in the early twenty-first century compared with previous generations is caused by overreactions of immune systems that have not been sufficiently challenged by previous exposure to allergens. Which of the following types of information would be most consistent with this hypothesis?
- data that show a correlation between a high frequency of asthma in adults and the absence of pets in their childhood environments
- evidence that a mechanism exists that explains how animal allergens can induce asthma in both adults and children
- data that show that adults living with household pets are more likely to have asthma than adults living in households without pets
- evidence that children living with household pets are more likely to develop asthma than those living without household pets
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the interpretation of scientific data. The investigator's hypothesis links an increase in the frequency of adult asthma with a decrease in allergen exposure during childhood. Data showing a correlation between adults diagnosed with asthma and an absence of pets in their childhood environments would be the strongest evidence to support the investigator's hypothesis.
Objective 0002
Central Concepts and Connections in Science (Standard 2)
2. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that causes AIDS probably originated in chimpanzees in central Africa and began appearing in humans between 1915 and 1940. The first cases of AIDS were diagnosed in the early 1980s. Which of the following was most likely responsible for the subsequent worldwide spread of the virus?
- Improved transportation facilitated greater movement of humans around the world.
- Rapid encroachment on chimpanzee habitat increased the frequency with which humans contracted the virus.
- New technology facilitated the recognition and diagnosis of the disease.
- Blood transfusions became more widely available and provided a new route for transmission of the virus.
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the social, cultural, and ethical aspects of science. An increase in the availability and affordability of different modes of transportation between 1915 and 1980 led to an increase in both domestic and international travel. This increase in travel has contributed to the worldwide spread of viruses like HIV.
Objective 0003
Cellular Chemistry and Structure (Standard 3)
3. CAM and C4 photosynthesis are similar in that both processes:
- utilize photosystem II instead of photosystem I.
- provide an alternative pathway for the polymerization of glucose into starch.
- bypass the Calvin cycle and the production of 3-phosphoglycerate.
- increase the concentration of CO2 in photosynthesizing tissues.
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the biochemical pathways involved in photosynthesis. In CAM photosynthesis, CO2 is taken up by photosynthesizing cells at night and is temporarily fixed into organic compounds. During the day, the CO2 is released and used in the Calvin cycle. In C4 photosynthesis, CO2 is temporarily fixed into an organic acid in mesophyll cells. These organic acids are then transported to photosynthesizing cells and release CO2 for use in the Calvin cycle. Both of these processes have the same effect: they increase the concentration of CO2 in photosynthesizing cells.
Objective 0003
Cellular Chemistry and Structure (Standard 3)
4. The extensive development of Golgi apparatus is most likely to be found in which of the following types of cells?
- apical meristem tissue cells in the tips of roots
- vertebrate muscle cells with high aerobic demands
- light-sensitive cells in the compound eyes of insects
- mammalian cells specialized for secreting hormones
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the functions of organelles. The Golgi apparatus is an organelle that consists of a stack of flattened vesicles called cisternae. Proteins that enter the Golgi apparatus are modified by enzymes found in the cisternae, and many of the modified proteins are later transported outside of the cell. A cell that is specialized for secreting hormones would likely contain a large number of Golgi apparatus.
Objective 0004
Organisms (Standard 4)
5. Sponges are animals composed of relatively unspecialized cells. This characteristic of sponges best accounts for their:
- lack of body symmetry.
- filter feeding habit.
- lack of true tissues.
- sessile lifestyle.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the hierarchical levels of organization in multicellular organisms. True tissues consist of cells from the same origin that work together to carry out a specific function. Sponges lack functionally specialized cells and as a result lack true tissues.
Objective 0004
Organisms (Standard 4)
6. The primary function of phloem tissue in a green plant is to:
- carry water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.
- provide undifferentiated cells that contribute to primary growth.
- transport sugars and other nutrients throughout the plant.
- convert cellular waste products into harmless compounds.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the function of different types of tissues in organisms. Phloem is one type of tissue found in the vascular system of green plants. Its function is to transport sugars and other nutrients throughout the plant.
Objective 0004
Organisms (Standard 4)
7. Which of the following is the best example of a homeostatic mechanism regulating a biological system?
- The ability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen molecules changes according to variations in the partial pressure of dissolved oxygen in blood.
- The growth rates of plants change according to the availability of freshwater.
- The number of Batesian mimics in an ecosystem changes as a result of changes in the numbers of available models in the ecosystem.
- Musculature and cardiovascular capacity change in response to increased exercise in mammals.
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the processes and strategies used by organisms to maintain homeostasis. Homeostatic mechanisms help biological organisms maintain a steady internal environment when confronted with changing internal or external conditions. For example, under conditions of high partial pressure of oxygen, such as in the lungs, the binding of oxygen by hemoglobin is high and oxygen is taken up. Conversely, under conditions of low partial pressure of oxygen, such as would be found in metabolically active tissues, the ability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen is low and oxygen is released. This mechanism ensures that an organism can rapidly respond to internal changes in the need for oxygen.
Objective 0005
Interdependence (Standard 5)
8. The net primary productivity of an ecosystem can be viewed as the:
- standing biomass of all trophic levels.
- amount of energy available to the consumers.
- new growth of all consumers and producers.
- total biomass available to the decomposers.
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the flow of energy and the cycling of matter through ecosystems. The primary productivity of an ecosystem is equal to the amount of light energy that is converted into chemical energy per unit time by primary producers. Some of this chemical energy is used by primary producers to sustain their metabolic processes. The difference between these two values is the net primary productivity, and it represents the amount of energy that is available to consumers in an ecosystem.
Objective 0005
Interdependence (Standard 5)
9. Use the soil food web below to answer the question that follows.
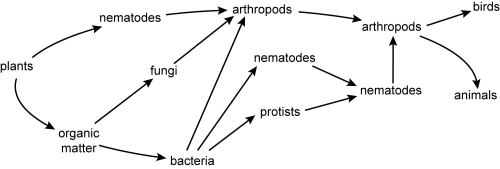
If predator-prey relationships are assumed to exist only between animals, how many different predator-prey relationships are shown in the food web, and on how many different trophic levels do predators occur?
- 6 predator-prey relationships on 4 trophic levels
- 6 predator-prey relationships on 3 trophic levels
- 7 predator-prey relationships on 3 trophic levels
- 7 predator-prey relationships on 4 trophic levels
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the interdependence of organisms within a food web. There are six predator-prey relationships in the food web. They are arthropods consuming nematodes; nematodes consuming nematodes; arthropods consuming arthropods; arthropods consuming nematodes; birds consuming arthropods; and animals consuming arthropods. Trophic levels are described in terms of how far they are removed from the primary producers at the base of a food chain (decomposers that feed on detritus are not counted). For example, in the food chain at the top of the diagram, plants represent the producers, the nematodes are primary consumers (herbivores), while arthropods represent secondary and tertiary consumers, and birds represent quaternary consumers. Thus the predators occupy three trophic levels.
Objective 0006
Heredity and Genetics (Standard 6)
10. In a population consisting of 800 individuals of an insect species, there are only two alleles for the gene locus that determines eye color. One allele is dominant to the other. There are 250 homozygous dominant, 400 heterozygous, and 150 homozygous recessive individuals. What is the approximate frequency of the recessive allele in the gene pool of this population?
- 31%
- 38%
- 44%
- 56%
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the patterns of inheritance and their application to genetics problems. Each individual in the population of 800 (250 + 400 + 150) has two gene loci that can be occupied by alleles, so there are 1600 (2 × 800) loci present. The 250 homozygous dominant individuals total 0 recessive alleles among them. The 400 heterozygous individuals possess a total of 400 recessive alleles, and the 150 homozygous recessive individuals have 300 recessive alleles. Thus the total number of recessive alleles present in the population is 700 (0 + 400 + 300), and the approximate frequency of the recessive allele in the population is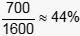 .
.
Objective 0006
Heredity and Genetics (Standard 6)
11. In order to produce large quantities of insulin, human growth hormone, or other valuable medical compounds, genetic engineers use which of the following procedures?
- applying the polymerase chain reaction to a recombinant plasmid
- cutting human DNA with restriction enzymes and inserting recombinant plasmids
- identifying recombinant plasmids using a DNA microarray assay
- inserting recombinant plasmids into bacterial cells that then multiply
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the basic principles, methods, and applications of genetic engineering. Plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules found primarily in bacteria cells. They are distinct from the bacterial genome, can be transferred to other bacteria, and replicate independently. Genetic engineers use plasmids as vectors to carry genetic material into bacterial cells. Genes can be added to plasmid DNA using restriction enzymes and the resulting recombinant plasmid can then be inserted into bacterial cells. The bacteria containing the plasmids then multiply and produce copies of the gene of interest.
Objective 0007
Evolution (Standard 7)
12. The idea that species are generally well adapted to their environments because the ecosystems they inhabit are stable over long periods of time is a basic tenet of which of the following theories of evolution?
- punctuated equilibrium
- natural selection
- uniformitarianism
- biological species concept
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of modern evolutionary theory. Punctuated equilibrium is a theory of evolution that proposes that species diverge relatively rapidly (in geologic terms) and then stay the same for longer periods of time. If the new species is well adapted to its environment and that environment is stable, the species may not change much for long periods of time as a result of stabilizing selection.
Objective 0007
Evolution (Standard 7)
13. James Hutton's theory of gradualism and Charles Lyell's theory of uniformitarianism played significant roles in the development of evolutionary theory, because together they influenced Charles Darwin by persuading him that:
- the occurrence of continental drift provides an explanation for the discovery of similar species on different landmasses.
- the common ancestry of all living organisms explains their fundamental similarity.
- Earth is old enough that changes through natural selection could account for the evolution of species.
- transitional forms in the fossil record provide links between distinct species.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of modern evolutionary theory and its historical development. The theory of gradualism was developed to explain the geologic features on Earth. This theory maintained that slow steady processes, such as a river carving through rock, could lead to substantial changes in the landscape. Uniformitarianism expanded the theory of gradualism by suggesting that the types of geologic processes that shaped Earth's surface have remained the same throughout Earth's history. The use of these theories to explain the wide variation in landforms on Earth's surface led scientists to conclude that the Earth was very old. This realization played a significant role in the development of evolutionary theory because it supported the idea that the Earth was old enough for species to have evolved through natural selection.
Objective 0007
Evolution (Standard 7)
14. Use the cladogram below to answer the question that follows.
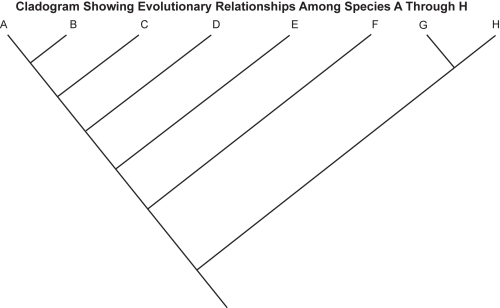
Which of the following conclusions about the evolutionary relationships of species A–H can be drawn from the cladogram shown?
- Species F is more closely related to species H than species F is to species D.
- Species D is more closely related to species E than species D is to species C.
- Species F is more closely related to species A than species F is to species G.
- Species D is more closely related to species A than species D is to species B.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of systems of taxonomic classification. Each branch point in a cladogram represents the divergence of two species from a common ancestor and the location of each branch indicates how recently this divergence occurred. In the given cladogram, Species A and F share a common ancestor, the second branch point from the bottom of the main evolutionary line. Since species G and H derive from an ancestor that diverged from the main line at an earlier point, they do not share a direct common ancestor withspecies F.
Objective 0008
Science Instruction and Assessment (Standard 8)
15. A biology teacher is planning to discuss the conservation of matter and energy as part of a presentation on ecosystems but discovers that students have a poor conceptual understanding of the physical science concept of entropy. Which of the following activities would be the most effective for helping students develop a conceptual understanding of entropy in biological systems?
- calculating the amount of energy transferred from the sun to primary producers, consumers, and predators in a local ecosystem
- creating a compost bin as a model ecosystem and using it to measure the breakdown of organic matter and the heat generated by decay
- identifying everyday examples of heat loss that effectively demonstrate the second law of thermodynamics in a closed system
- comparing the amount of energy transferred between trophic levels in an ecosystem with the amount of mass that is transferred between levels
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of instructional strategies for promoting students' development of conceptual understanding. Isolated systems spontaneously evolve towards the state of maximum entropy, which occurs at thermodynamic equilibrium. The diminishing mass of the compost over time, accompanied by the loss of heat energy, eventually results in a thermodynamically stable system that represents a state of maximum entropy. The measurable changes in the compost thus provide a good example of entropy that will be hands-on and accessible to students.