Study Guide
Field 038: Reading
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
Objective 0001
Theoretical and Research Foundations of Reading Development (Standard 1)
1. Which of the following conclusions about dyslexia can best be drawn based on the results of recent scientific, longitudinal studies that used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to monitor brain activation of skilled and dyslexic readers during reading?
- The root cause of dyslexia is physiological and can often be prevented through the use of appropriate dietary supplements.
- Dyslexia can be identified neurologically and effectively treated through explicit, intensive instructional intervention.
- Lack of neurobiological evidence for dyslexia suggests that future research should focus on prevention rather than on a cure.
- Most children with dyslexia tend to outgrow it by late adolescence or early adulthood with or without remediation.
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate an understanding of findings of research foundations of reading development, such as results of scientific neurological studies of skilled and dyslexic readers. Longitudinal research studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) indicate that skilled and dyslexic readers activate different regions of the brain during reading. As children get older, skilled readers continue to activate the same brain region during reading, while dyslexic readers who receive no treatment (or ineffective treatment) increasingly activate other brain regions. However, dyslexic readers who receive effective, intensive instructional intervention begin to activate the same brain region during reading as skilled readers.
Objective 0002
Foundations of Scientifically Based Reading Instruction (Standard 2)
2. Which of the following steps would be most appropriate for a classroom teacher to take to address the needs of a student who does not meet grade-level expectations on a Tier 1 pre-assessment in a key component of reading?
- placing the student in a Tier 2 reading program
- using assessment data to design differentiated reading instruction for the student
- referring the student for special support services in reading
- using assessment data to design an intensive, targeted reading intervention for the student
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate an understanding of components of effective evidence-based intervention and extension programs, including Indiana's Response to Instruction (RtI) model. According to Indiana's RtI model, classroom teachers are expected to administer a pre-assessment prior to planning core instruction. Students who do not meet grade-level expectations on the pre-assessment should receive differentiated instruction that is specifically designed to address their evidence-based needs (i.e., needs identified through an analysis of the results of the pre-assessment and other relevant assessments).
Objective 0003
Foundations of Reading Assessment (Standard 3)
3. A teacher conducts targeted reading assessments with a student at frequent, regular intervals, plots the student's results on a graph, and tracks the student's progress by comparing the student's plot line with respect to his or her aim line. According to Indiana's Response to Instruction (RtI) model, these assessment components would be most appropriate to use in which of the following contexts?
- when conducting a diagnostic battery
- in conjunction with Tier 1 instruction
- when conducting a summative assessment
- in conjunction with Tier 2 instruction
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate an understanding of components and features of a comprehensive reading assessment system as defined by Indiana's Response to Instruction (RtI) model, such as use of consistent progress monitoring and appropriate documentation of assessment results. The teacher's actions in the scenario represent key steps of the decision-making process involved in targeted reading instruction beyond the core curriculum. In Indiana's RtI model, a teacher must regularly monitor and record the progress of a student receiving targeted Tier 2 instruction to ensure that the intervention is effective and the student is progressing toward achieving grade-level expectations in the given area of reading.
Objective 0004
Phonemic Awareness (Standard 4)
4. The results of informal assessments indicate that a student in a first-grade class who has been receiving targeted Tier 3 support in phonological awareness is ready to begin instruction in phonemic awareness. The teacher asks the reading coach to help plan appropriate strategies to use with the student. Which of the following strategies would be most appropriate for the reading coach to recommend for this purpose?
- helping the student identify the objects shown on picture cards and sort the cards according to the beginning sound of each object's name
- having the student listen to a list of familiar words (e.g., animal, cat, zebra) and then repeat each word while clapping out its syllables
- reading aloud to the student from a variety of illustrated "big books" that feature rhyming words and helping the student generate matching rhymes
- saying a simple word to the student (e.g., lay) and modeling how to make a new word by adding another sound to it (e.g., play, clay)
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the phonological- and phonemic-awareness skills continuum. The student is described as being "ready to begin instruction in phonemic awareness." This implies that the student has demonstrated mastery of phonological-awareness skills that fall earlier along the phonological- and phonemic-awareness continuum. The earliest phonemic-awareness skills involve identifying beginning, medial, and final phonemes in simple words presented orally. Having the student name the objects shown on picture cards and then sort the cards according to the beginning sound of each object's name would be an effective strategy for helping the student begin to focus on the initial phonemes of words.
Objective 0004
Phonemic Awareness (Standard 4)
5. A reading teacher is working with a small group of high school students who are struggling to decode new academic vocabulary from their various content-area classes. In addition to using word study strategies, the reading teacher also engages the students in a variety of oral activities such as having them slowly orally break up similar-sounding words into syllables (e.g., hy/dro/sphere, hy/per/bo/le, hy/poth/e/sis) or having them add or delete a sound to make a different word (e.g., evolution + /r/ = revolution). These types of activities help strengthen the students' word learning primarily by:
- reinforcing their knowledge of common phonics patterns.
- developing their morphological-analysis skills.
- activating their phonological and phonemic awareness.
- focusing their attention on denotative processes.
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of key concepts and scientifically based reading research in phonemic awareness, such as the critical role of phonemic awareness in learning to read an alphabetic language; and the importance of providing explicit, systematic instruction in phonological and phonemic awareness. Breaking up words presented orally into syllables is a phonological-awareness skill that can reinforce older students' ability to segment words into recognizable chunks, or syllables. Adding or deleting a phoneme to a word presented orally is a phonemic-awareness skill that can promote students' ability to build new words, as well as enhance their ability to distinguish differences between similar-sounding words. Having struggling high school students practice these basic phonological- and phonemic-awareness skills helps promote their development of effective decoding and encoding skills.
Objective 0005
Phonics (Standard 5)
6. In an informal assessment, a reading teacher has a third-grade student read aloud an unfamiliar passage while the teacher makes notes about the student's performance on a photocopy of the text. An excerpt of the teacher's annotated text appears below.
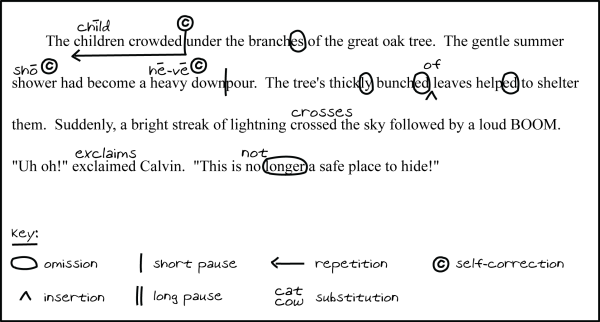
Based on the assessment evidence provided, the student would likely benefit most from an intervention focused on improving the student's:
- attention to word endings.
- knowledge of common vowel teams.
- use of syllabication skills.
- ability to self-monitor for meaning.
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate the ability to provide SBRR-based, evidence-based, and developmentally appropriate assessment and instruction in the accurate, automatic decoding of words containing inflectional endings. The student demonstrates a clear pattern of errors with regard to attention to word endings. The student omits inflectional endings in several words (e.g., branches, thickly, bunched, helped) and substitutes a different ending in some other words (e.g., crossed becomes crosses, exclaimed becomes exclaims). The student's performance suggests a weakness in decoding accuracy with respect to word endings.
Objective 0005
Phonics (Standard 5)
7. A reading coach is helping a new kindergarten teacher plan a series of lessons for a small group of advanced learners who are ready to begin sounding out and blending the sounds of simple printed words. Which of the following guidelines would be most important for the teacher to follow during these initial lessons?
- emphasizing familiar words to which the students have had frequent exposure in environmental print
- teaching a diverse mixture of single-syllable words that illustrate a range of phonics elements and spelling patterns
- making sure to include some challenging words that are not yet part of the students' oral vocabularies
- focusing on regular words containing letters the students have mastered in letter-sound correspondence tasks
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate the ability to provide SBRR-based, evidence-based, and developmentally appropriate instruction in phonics. A key principle of beginning phonics instruction in a research-based reading program is to focus initial instruction on regular words (i.e., each letter of the word represents its most common sound) that are relatively short (i.e., contain only two or three phonemes). Regular word-reading instruction can begin as soon as students have mastered a handful of high-frequency letter-sound correspondences and have developed phonemic segmenting and blending skills.
Objective 0006
Fluency (Standard 6)
8. A sixth-grade teacher has a small group of students who have been identified through formal and informal fluency assessments as having a low reading rate but a high accuracy rate. The teacher asks the reading coach to recommend an appropriate intervention. Which of the following strategies would be most effective in addressing the students' needs?
- engaging the students frequently in choral reading and echo reading activities led by a proficient reader
- having the students silently read a wide range of texts at their independent level to build automaticity
- encouraging the students to practice reading aloud with an adult who can provide corrective feedback
- arranging for the students to participate in buddy reading with high school students to build confidence
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate the ability to provide SBRR-based, evidence-based, and developmentally appropriate intervention in fluency. Students who read slowly but accurately need to improve their ability to decode text automatically. Reading texts at their independent-reading level provides students with practice reading texts that they can easily decode, which allows them to focus on improving their reading rate. Research has shown that while rereading the same text builds reading rate and comprehension with respect to that text, it is not generalizable to other texts. Reading a wide range of independent-level texts, however, has proven to be effective in promoting automaticity in decoding.
Objective 0007
Vocabulary and Academic Language (Standard 7)
9. Which of the following language competencies would provide the best indicator that a student has an established knowledge of a particular vocabulary word?
- The student can recognize the morphological structure of the word and associated words with shared morphological elements.
- The student can use the word appropriately in expressive contexts.
- The student can associate the word with a specific meaning or with a semantically related word (e.g., a synonym, an antonym).
- The student can understand the word in a targeted written context.
- Answer
- Correct Response: B.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate the ability to provide SBRR-based, evidence-based assessment and progress monitoring in word study. Being able to use a word correctly in various contexts demonstrates word knowledge that reflects deep processing. Research has shown that students who engage in active processing of words are more likely to comprehend texts that contain those words.
Objective 0007
Vocabulary and Academic Language (Standard 7)
10. An eighth-grade English Learner who has an advanced level of proficiency in English and who demonstrates grade-level mastery of complex language structures struggles to understand the following passage.
When it comes to professional sports, there's more to winning than natural talent and hard work. Why do some professional athletes win one championship after another, while others can only hope to win once or twice in a lifetime? Champions have heart, a kind of courage or stubbornness that comes to the fore when it matters most. And that makes all the difference.According to the student's profile and the passage, which of the following language factors is the most likely cause of the student's comprehension difficulty?
- limited understanding of general academic vocabulary
- difficulty interpreting conjunctions and interrogative pronouns
- limited knowledge of idiomatic expressions in English
- difficulty linking personal pronouns to their antecedents
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of key concepts in the development of vocabulary. The passage shown contains several expressions that are idiomatic in English and that may not be interpreted literally. For example, "when it comes to _____," "there's more to _____ than _____," "one _____ after another," "can only hope to _____," "have heart," "_____ that comes to the fore," and "_____ makes all the difference" are all idiomatic expressions that could challenge an advanced English Learner who is unfamiliar with their meaning or usage.
Objective 0008
Comprehension and Analysis of Informational and Persuasive Texts (Standard 8)
11. A high school reading teacher has provided students with direct instruction in using semantic mapping to support the study of literature and would like to deepen their knowledge of and competence in applying this skill. Which of the following steps would likely be most effective for the reading teacher to take for this purpose?
- including practice in semantic mapping as an integral feature of literature discussions for the remainder of the school year
- providing students with a variety of graphic organizers suitable for preparing semantic maps about a range of academic and nonacademic topics
- posting a set of directions for creating a semantic map in the classroom, as well as representative examples
- collaborating with content-area teachers to provide the students with instruction and practice in semantic mapping across the curriculum
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate the ability to provide SBRR-based instruction in comprehension strategies that students can use independently to support their own understanding and skilled analysis of informational and persuasive texts. Providing students with guided and independent practice applying a new reading skill or strategy is an essential component of effective reading instruction and reflects research-based best practices. By collaborating with content-area teachers to reinforce a specific reading strategy with students, the reading teacher provides students with additional practice opportunities designed to enhance their understanding of the strategy and their facility in applying it to new situations.
Objective 0008
Comprehension and Analysis of Informational and Persuasive Texts (Standard 8)
12. A middle school reading teacher is planning instruction in evaluating the reasoning of a persuasive text. Guided analysis focused on which of the following aspects of the text would be most important to include in a lesson for this purpose?
- the writer's use of references, such as a bibliography
- the writer's voice as reflected in vocabulary and stylistic choices
- the writer's explicit argument and supporting evidence
- the writer's use of graphic features, such as tables or diagrams
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate the ability to use SBRR-based, evidence-based instruction to scaffold and facilitate students' analysis of persuasive texts. In evaluating the reasoning of a persuasive text, students must analyze factors such as the author's logic in developing an effective argument or thesis, the author's use of evidence to support the argument or thesis, and the credibility of the evidence the author presents.
Objective 0009
Literary Texts (Standard 9)
13. After reading independent-level fictional narratives, a sixth-grade student typically can recall many details from a story but has difficulty summarizing the story's plot. Which of the following interventions would likely be most effective for the reading teacher to use to address the student's learning needs in text comprehension?
- using a dialogue journal to respond to the student's questions about particular texts
- guiding the student in methods for previewing or skimming a text in order to set a purpose for reading
- providing the student with explicit instruction in common narrative text structures
- assigning writing prompts that focus the student's attention on thematic concerns of the texts
- Answer
- Correct Response: C.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of predominant text structures used in literary texts, and the ability to use SBRR-based strategies to improve students' application of these text structures to support their reading comprehension and analysis of literary texts. Different types of narrative texts follow different story grammars. For example, a mystery unfolds differently than a fable or a biography. Understanding these story grammars, or narrative text structures, can help students identify the key elements of a story, including the story's plot structure.
Objective 0010
Literacy-Rich Classroom Environment (Standard 10)
14. Which of the following strategies for creating a classroom library would be most important to apply to help foster a literacy-rich classroom environment?
- spreading books around the classroom so that students in any section of the room have equal access to them
- gathering multiple copies of each book selection so that students can read in small groups if they choose
- organizing the books alphabetically by author's last name to facilitate students' ability to locate texts of interest
- including books at multiple reading levels that represent a variety of cultures, genres, topics, and text types
- Answer
- Correct Response: D.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate an understanding of skills and strategies for creating and maintaining a physical environment that promotes the reading development of all students. The goal of a literacy-rich classroom environment is to build a community of readers and writers who have positive attitudes toward literacy and develop lifelong habits of engaging in literacy-related activities. Research has shown that students are more likely to engage in reading independently when books and other reading materials are physically easily accessible, such as in a classroom library; are comprehensible, in that they match students' reading abilities; and are interesting, in that they address students' range of interests and reflect diverse settings and cultures.
Objective 0011
Professional Learning and Leadership in Reading (Standard 11)
15. A reading teacher has completed a school-wide needs assessment in reading. The school's literacy committee reviews the results of the assessment and decides to focus professional development efforts on two specific areas. Which of the following steps should the reading teacher take next in this process?
- establishing specific goals for the professional development plan
- gathering information about weaknesses in the school's reading program
- planning an in-service workshop in one of the two areas as soon as possible
- demonstrating model reading lessons that teachers can use in their classrooms
- Answer
- Correct Response: A.
This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of literature and research on organizational change and adult learning as they relate to professional development in reading. There are many different models of professional development, such as explicit training, involvement in an improvement process, study groups, action research, and mentoring. Each model has its advantages and disadvantages and may be more effective than others in specific contexts. Defining the goals of a professional development effort will help the reading teacher define the context and make more effective decisions about the type and scope of the professional development.
Directions for the Video Assignment
Each question in this test is a multiple-choice question with four answer choices. Read each question and answer choice carefully and choose the ONE best answer.
This test contains one or more multiple-choice questions related to a video that will be presented on the screen. Review the test question and then when you are ready to view the video, put on your headset and select the
button on the video display box. You may pause, stop, and replay the video as necessary using the
buttons on the screen.
Try to respond to all questions. Even if you are unsure of an answer, it is better to guess than not to respond at all.
Sample Video Assignment

On each test, examinees will watch a video of a classroom teacher providing instruction to a group of students, and then respond to a multiple-choice question about the teacher's performance. The video may depict a whole-class lesson, a teacher working with a small group of students, or a teacher helping an individual student one-on-one. Before watching the video, examinees will have an opportunity to review the multiple-choice question accompanying the video. Once the video is completed, examinees will respond to the question.